reed-sternberg cells|reed sternberg cell function : Clark Reed-Sternberg cells are large, abnormal lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) that may contain more than one nucleus. These cells are found in people with Hodgkin .
Tele Sena - Home. Entre ou Cadastre-se. 0. PagSeguro é a forma mais eficiente e segura de efetuar e receber pagamentos online.
0 · which is worse hodgkin's or non
1 · types of reed sternberg cells
2 · reed sternberg cells treatment
3 · reed sternberg cells pictures
4 · reed sternberg cells pathology outlines
5 · reed sternberg cells are present
6 · reed sternberg cell pdf
7 · reed sternberg cell function
8 · More
Resultado da 2 dias atrás · Notícias de Ivinhema, Angélica, Novo Horizonte do Sul e Vale do Ivinhema - Ivi Notícias
reed-sternberg cells*******Reed-Sternberg cells are the hallmark tumor cells of Hodgkin lymphoma. They represent less than 1% of the tumor tissue, .reed-sternberg cellsReed–Sternberg cells (also known as lacunar histiocytes for certain types) are distinctive, giant cells found with light microscopy in biopsies from individuals with Hodgkin lymphoma. They are usually derived from B lymphocytes, classically considered crippled germinal center B cells. In the vast majority of cases, the immunoglobulin genes of Reed–Sternberg cells have undergone both V(D)J recombination Classical Hodgkin lymphoma is the more common type of this disease. People diagnosed with this type have large lymphoma cells called Reed-Sternberg cells .
Reed-Sternberg cells are abnormal lymphocytes found in Hodgkin lymphoma. Learn about their origin, features, and the controversy over their discovery .
Reed-Sternberg cells are generated by incomplete cytokinesis and refusion of Hodgkin cells. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) plays a major role in the rescue of .
Reed-Sternberg cells are large, abnormal lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) that may contain more than one nucleus. These cells are found in people with Hodgkin .
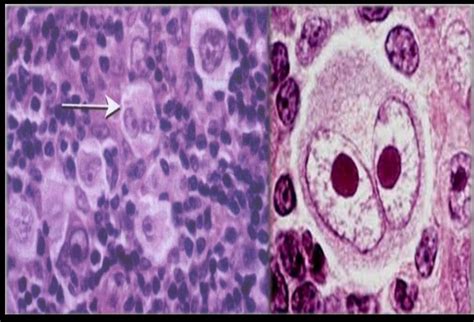
Learn about Reed-Sternberg cells, the large, bi- or multinucleated cells that are the hallmark of Hodgkin lymphoma. Find out their origin, immunophenotype, genetics, . Reed–Sternberg (RS) cells in HL have distinctive large cell morphology, are characteristic of the disease and their presence is essential for diagnosis. Enlarged . Reed–Sternberg (RS) cells in HL have distinctive large cell morphology, are characteristic of the disease and their presence is essential for diagnosis. Enlarged .
The Reed-Sternberg cell is essential for an unequivocal diagnosis of Hodgkin’s disease [1, 2] and therefore is generally accepted to represent the malignant cell of Hodgkin’s . Description. Reed-Sternberg cells are large, abnormal lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) that may contain more than one nucleus. These cells are found in people with Hodgkin lymphoma. .

Hodgkin and Reed–Sternberg (HRS) tumour cells of classic Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) are morphologically characterized by extensive eosinophilic cytoplasm and typically two multilobated nuclei (Reed .
However, Reed-Sternberg cells make up only a small part of a Hodgkin lymphoma tumor, and the rest of the tumor is made of normal lymphocytes, which can cause inflammation. If your doctor suspects you have Hodgkin lymphoma, he or she will recommend a surgical biopsy rather than a needle biopsy to make a diagnosis. The cells that are a hallmark of this disease — the mononucleated Hodgkin cells and the multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells — were first described by Dorothy Reed and Carl Sternberg around .
reed-sternberg cells reed sternberg cell functionThe Reed-Sternberg cell is essential for an unequivocal diagnosis of Hodgkin’s disease [1, 2] and therefore is generally accepted to represent the malignant cell of Hodgkin’s disease (Table 1). The frequency of diagnostic Reed-Sternberg cells increases with advanced clinical stages of disease [3] and with progression of Hodgkin’s disease .
Reed-Sternberg cells have been convincingly shown to be of B-cell lineage although they have an unusual and characteristic phenotype (CD30 +, CD15 +, fascin+, LCA-). CD30 expression is results in activation of NFκB signaling in RS cells. RS cells often express CD40 on their surface, and binding of CD40 ligand (soluble or expressed on T cells . Reed-Sternberg cells are a classical finding diagnostic of Hodgkin lymphoma. They are giant, multinucleated cells with abundant pale cytoplasm. Reed-Sternberg cells are rare, making up <1% of lymphoid tissue, with the background consisting of lymphocytes, plasma cells, eosinophils and macrophages.Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition was named after the English physician Thomas Hodgkin, who first described it in 1832. Symptoms may .Classical Hodgkin lymphoma is characterized by the presence of both Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma is characterized by the presence of lymphocyte-predominant cells, sometimes termed “popcorn cells,” which are a variant of Reed-Sternberg cells. It is important to know your subtype since it .Reed-Sternberg cell. Reed-Sternberg cells are large, abnormal lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) that may contain more than one nucleus. These cells are found in people with Hodgkin lymphoma. Reed-Sternberg cells are also called Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. None - This image is in the public domain and can be freely reused. Reed-Sternberg cells are a classical finding diagnostic of Hodgkin lymphoma. They are giant, multinucleated cells with abundant pale cytoplasm. Reed-Sternberg cells are rare, making up <1% of lymphoid tissue, with the background consisting of lymphocytes, plasma cells, eosinophils and macrophages.
Reed-Sternberg-like cells have phenotypes that are remarkably similar to those of conventional Reed-Sternberg cells. In this interesting case report, we discuss a case of disseminated B-cell Non-Hodgkin lymphoma with Reed-Sternberg-like cells that presented as a diagnostic challenge. It is essential to distinguish between classical .
Hodgkin and Reed/Sternberg (HRS) cells are the hallmark cells of Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL). They are large, often multinucleated with a peculiar morphology and an unusual immunophenotype, that does not resemble any normal cell in the body. Despite their rarity in HL tissues, HRS cells are the clonal tumour cells of HL. There is indication from HL cell line studies that the mononuclear Hodgkin cells are the main proliferating tumor cells, whereas the Reed-Sternberg cells have little further proliferative capacity. 40 There might even exist a small subset among the Hodgkin cells that fulfill some criteria of cancer stem cells, although this is controversial. 41 .
Reed-Sternberg cells are a classical finding diagnostic of Hodgkin lymphoma. They are giant, multinucleated cells with abundant pale cytoplasm. Reed-Sternberg cells are rare, making up <1% of .
Reed-Sternberg-like cells have phenotypes that are remarkably similar to those of conventional Reed-Sternberg cells. In this interesting case report, we discuss a case of disseminated B-cell Non-Hodgkin lymphoma with Reed-Sternberg-like cells that presented as a diagnostic challenge. It is essential to distinguish between classical .Hodgkin and Reed/Sternberg (HRS) cells are the hallmark cells of Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL). They are large, often multinucleated with a peculiar morphology and an unusual immunophenotype, that does not resemble any normal cell in the body. Despite their rarity in HL tissues, HRS cells are the clonal tumour cells of HL. There is indication from HL cell line studies that the mononuclear Hodgkin cells are the main proliferating tumor cells, whereas the Reed-Sternberg cells have little further proliferative capacity. 40 There might even exist a small subset among the Hodgkin cells that fulfill some criteria of cancer stem cells, although this is controversial. 41 .The typical Reed-Sternberg cell has abundant cytoplasm and two or three nuclei, each with a single prominent nucleolus. The large size and unusual appearance of the Reed-Sternberg cell sets it apart from the adjacent smaller background cells. The mononuclear variants have nuclear and cytoplasmic features of Reed-Sternberg cells, but only have .Significant progress has been made in recent years in our understanding of the cellular origin of Hodgkin and Reed–Sternberg (HRS) cells in Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL). It is now clear that in most instances HRS cells represent clonal populations of transformed germinal centre (GC) B cells. While the tumour cells in the lymphocyte predominant type of the . The first cases of Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) were described by Thomas Hodgkin in 1832. A peculiar type of cells that is a hallmark of HL was first characterized in detail about 100 years ago by Dorothy Reed and Carl Sternberg. These cells are called Hodgkin cells when they are mononucleated and Reed/Sternberg cells when they are .
Lymphocyte-rich: Few Reed-Sternberg cells but many B cells. Lymphocyte-depleted: Numerous Reed-Sternberg cells plus extensive fibrosis. Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma has been reclassified as a non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma by the International Consensus Classification and is called nodular lymphocyte predominant B .reed sternberg cell function Hodgkin and Reed/Sternberg (HRS) cells have first been described as the hallmark cells in Hodgkin's disease (HD). They are called Hodgkin cells when they are mononucleated and Reed/Sternberg cells when they are multinucleated. They are named after Thomas Hodgkin, who first described cases of a lymphoid lesion in 1832 that was . Reed–Sternberg cells (RSCs) are hallmarks of classic Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL). However, cells with a similar morphology and immunophenotype, so-called Reed–Sternberg-like cells (RSLCs), are occasionally seen in both B cell and T cell non-Hodgkin Lymphomas (NHLs). In NHLs, RSLCs are usually present as scattered . A binucleate cell is an uncommon finding on cytosmears. The Reed-Sternberg (RS) cell is a diagnostic of Hodgkin's lymphoma (HL). Large binucleate cells resembling RS cells can be seen in a variety of benign and malignant conditions such as infectious mononucleosis, non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), melanoma, poorly .
Reed–Sternberg (RS) cells in HL have distinctive large cell morphology, are characteristic of the disease and their presence is essential for diagnosis. Enlarged cells are one of the hallmarks .
webkinechan2020. Kinechan FOTOS, VIDEOS E GIFS!. (196 arquivos) Foto de tudo, vídeo transando, fazendo duplo encarpado, chupeta e até canguru perneta ela faz) ACEITO .
reed-sternberg cells|reed sternberg cell function